
To get the memory size from /proc/meminfo, you can use the “MemTotal,” “MemFree,” and “Used” fields. To use this command, type “cat /proc/meminfo” at the command prompt. This command displays a detailed list of all of the system’s memory information. The “cat /proc/meminfo” command can also be used to check memory size in Linux. The free command provides information about both the physical. press the up or down arrow until the %MEM choice is highlightedĬheck memory size with cat /proc/meminfo command in Linux The free command allows you to display the amount of free and used memory on the system.press Shift+f to enter the interactive menu.Sort By memory Usage per-process in the interactive menu To use this command, simply type “top” at the command prompt. This command displays a list of all running processes, along with information on their CPU and memory usage. The “top” command is another way to check memory size in Linux. Swap: 3Check memory size with top command in Linux
Total used free shared buff/cache available You can print free memory by specifying seconds ‘-s’. 2) It could not make the memory that held the program free. And you want to track how much memory is getting utilized over the period. And if the program runs again, it will have to be loaded in from disk. This requires a specific operation to make it free, and a specific operation to allow it to be used again.
It can be seen by running the “cat /proc/meminfo” command. 1) It could make the memory that held the program free.
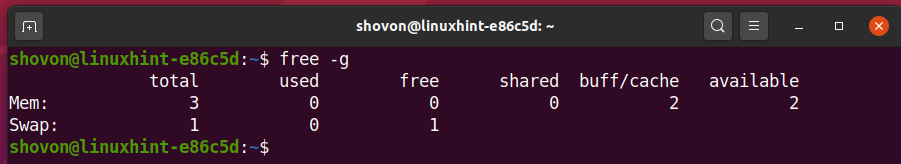
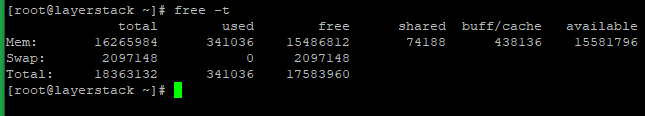
Cache Memory: This is a type of memory used by the kernel to cache files and directories. You can see how much swap space is available by running the “swapon” command. If your physical memory is full, Linux can move some data from physical memory to the swap space to make room. Swap Space: This is an area on your hard drive that Linux can use as virtual memory. It can be seen by running the “free” command. Under the Memory section, you will see the total amount of available memory, as well as the amount of used and free memory. Physical Memory: This is the actual RAM installed in your system. There are three primary types of memory in a Linux system: Display System Memory Free command used to check the used and available space of physical memory and swap memory in KB. When it comes to understanding RAM in Linux, you first need to know about the different types of memory. 10 Linux Free Command Examples This article provides some useful examples of free commands with options, that might be useful for you to better utilize memory that you have. 5 Ways To Check Available Memory In Linux Method 1: Using Ubuntu System Monitor Method 2: Using htop Method 3: Using the cat /proc/meminfo Command Method. These commands are “free,” “top,” and “cat /proc/meminfo.” Let’s take a look at each of them! Understanding RAM in Linux In this blog post, we will discuss three commands that will help you get this data. Do you ever wonder how much memory your system has? In Linux, there are a few different ways to check this information.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
